Terminals
In Linux environments, the terms ‘Shell’ and ‘Terminal’ are commonly used and although they are related, they actually refer to different things: A terminal (or terminal emulator) is a software program that provides a text-based interface to the shell, the program that processes user commands–which might also involve calling other programs–and returns the output.
Below is an expanded look at some commonly used terminal emulators and their key features.
 GNOME
GNOME
GNOME is the default terminal emulator for the GNOME desktop environment, widely used in many Linux distributions.
Key features
Profiles
Users can create multiple profiles, each with its own set of preferences, including colors, fonts, and keyboard shortcuts.
Tabs and Splitting
Supports opening multiple tabs and can split the terminal window into multiple panes.
Transparency and Backgrounds
Allows setting background images and adjusting the transparency of the terminal window.
Compatibility
Supports UTF-8 for a wide range of characters, making it suitable for international use.
 Konsole
Konsole
Konsole is part of the KDE desktop environment. It is known for its deep integration with KDE and its high degree of customizability.

Key features
Tabbed Interface
Allows multiple tabs within a single window, facilitating multitasking.
Profiles
Supports multiple profiles, enabling different settings for each session.
Split Views
Users can split Konsole windows horizontally or vertically.
Transparency and Theming
Supports background transparency and themes, which can be customized easily.
 iTerm2
iTerm2
iTerm2 is a replacement for Terminal and the successor to iTerm for macOS. It offers features beyond what traditional terminals provide.
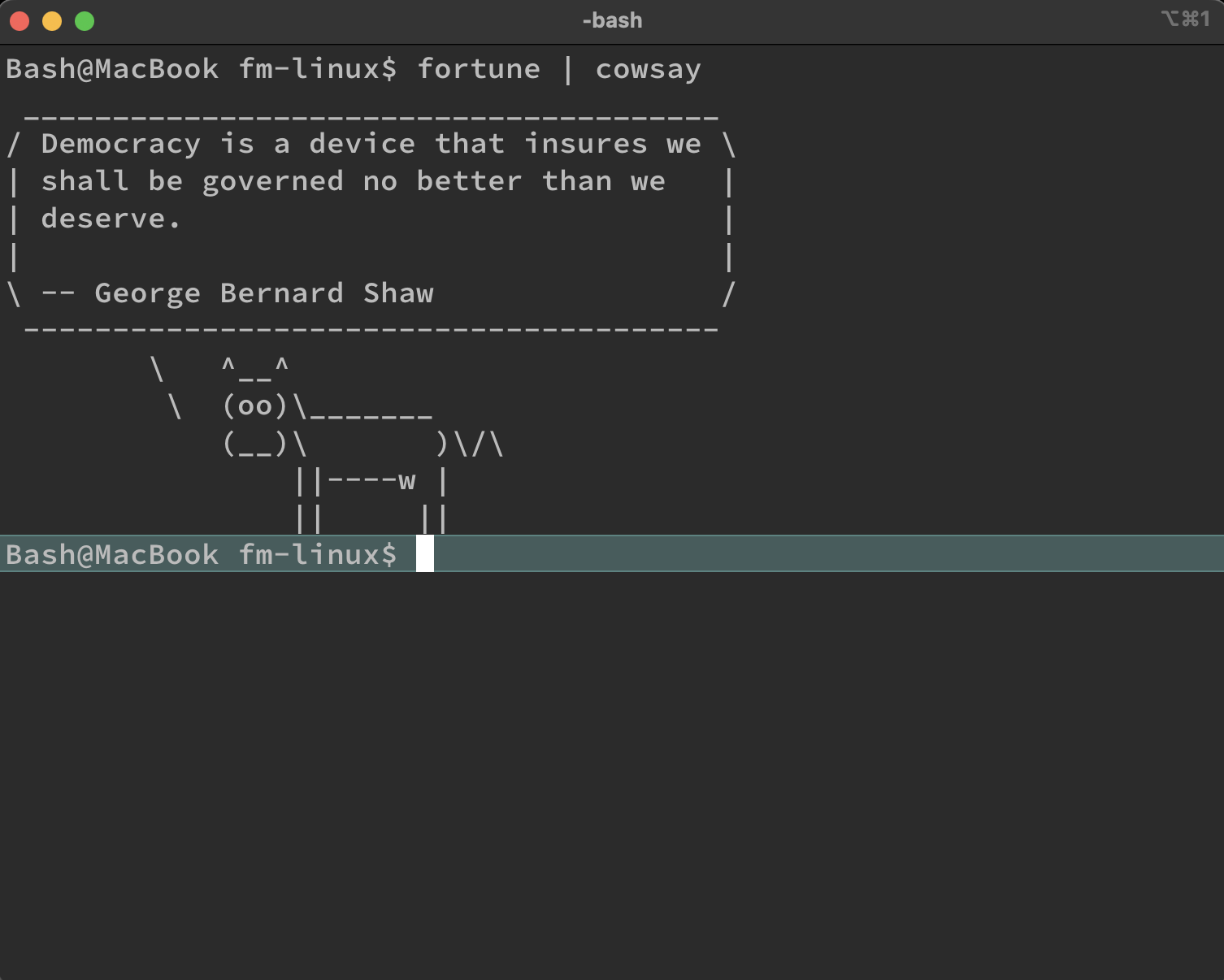
feature and cowsay in iterm2 on macOS
Key features
Split Panes
Users can divide iTerm2 into multiple panes, each with its own session.
Search
iTerm2 allows users to search through text and highlights occurrences.
Profiles
Supports detailed profiles, each with its custom colors, fonts, window transparency, and key bindings.
Advanced Paste Features
Offers a paste history and allows pasting with escape codes to avoid issues with unintended command executions.
Mouseless Copy
iTerm2 lets you use keyboard shortcuts to select and copy text without needing the mouse.
Shell Integration
iTerm2 can integrate with the shell to display badges, track command statuses, and more.
Trigger Support
Executes user-defined actions based on text output to the terminal.
Recap
Each of these terminal emulators offers unique features that cater to different needs and preferences, enhancing the user’s command-line experience. Whether you need deep customization, minimal resource usage, or advanced functionalities like search and shell integration, there’s a terminal emulator that fits the requirement.