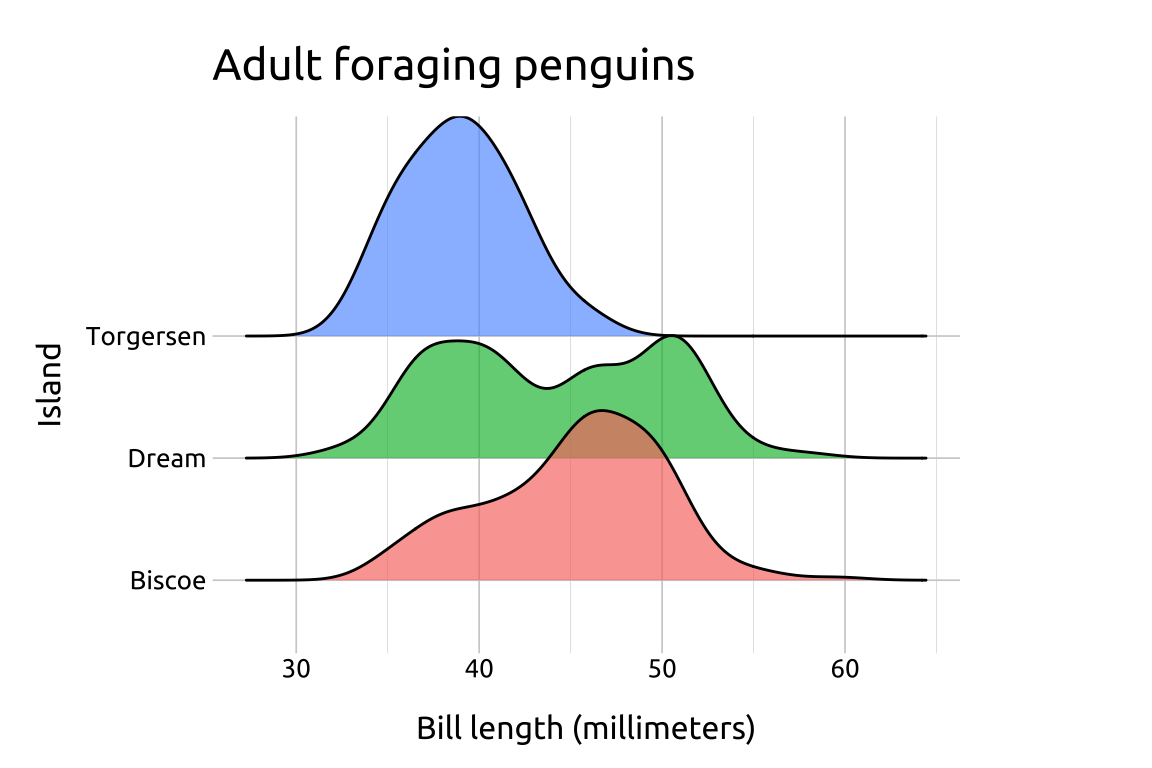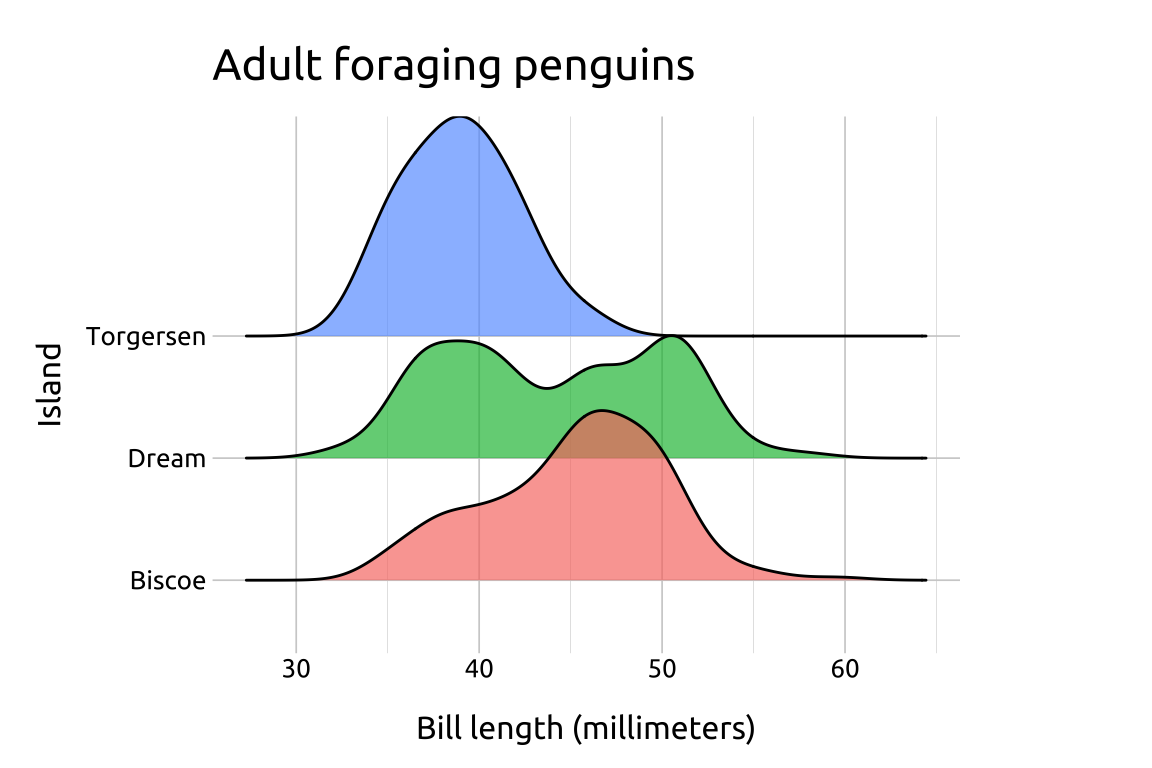
24 Ridgeline plots
24.1 Description
If we want to plot density curves but retain the interpretability of the axes, consider comparing multiple distributions using the ggridges package.
24.2 Set up
PACKAGES:
Install packages.
show/hide
install.packages("palmerpenguins")
library(palmerpenguins)
library(ggplot2)DATA:

Remove missing island from penguins
show/hide
peng_ridges <- filter(penguins, !is.na(island))
glimpse(peng_ridges)
#> Rows: 344
#> Columns: 8
#> $ species <fct> Adelie, Adelie, Adelie…
#> $ island <fct> Torgersen, Torgersen, …
#> $ bill_length_mm <dbl> 39.1, 39.5, 40.3, NA, …
#> $ bill_depth_mm <dbl> 18.7, 17.4, 18.0, NA, …
#> $ flipper_length_mm <int> 181, 186, 195, NA, 193…
#> $ body_mass_g <int> 3750, 3800, 3250, NA, …
#> $ sex <fct> male, female, female, …
#> $ year <int> 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007…24.3 Grammar
CODE:
Create labels with
labs()Initialize the graph with
ggplot()and providedataMap
bill_length_mmto thexaxisMap
islandto theyaxis andfillAdd the
ggridges::geom_density_ridges()layer (withalphaset to2/3)Remove the legend with
show.legend = FALSE
show/hide
labs_ridges <- labs(
title = "Adult foraging penguins",
x = "Bill length (millimeters)",
y = "Island", fill = "Island")
ggp2_ridges <- ggplot(data = peng_ridges,
aes(x = bill_length_mm,
y = island,
fill = island)) +
ggridges::geom_density_ridges(alpha = 2/3,
show.legend = FALSE)
ggp2_ridges +
labs_ridgesGRAPH:
Ridgeline plots are excellent for comparing continuous distributions across groups.